Standards and the Blue Economy
The seafood industry represents a critical source of food protein and global employment. In 2014, the overall trade value of the seafood sector was estimated at USD 140 billion, making it one of the most valuable non-petroleum products traded internationally.
The SSI Review: Standards and the Blue Economy takes a deep dive into the market and performance trends of the nine most prevalent seafood certification schemes operating in the wild catch and aquaculture sectors.
The review provides a reference point for buyers, producers, policy-makers and consumers in deciding how best to apply voluntary sustainability standards in their own decision-making processes.
This report was published in 2016 with data inclusive from 2008 to 2015.
80%
An estimated 80 per cent of all seafood is produced in developing countries, with more than 90 per cent of fishers and fish farmers being located in Africa and Asia.
Commodities Coverage
Highlights
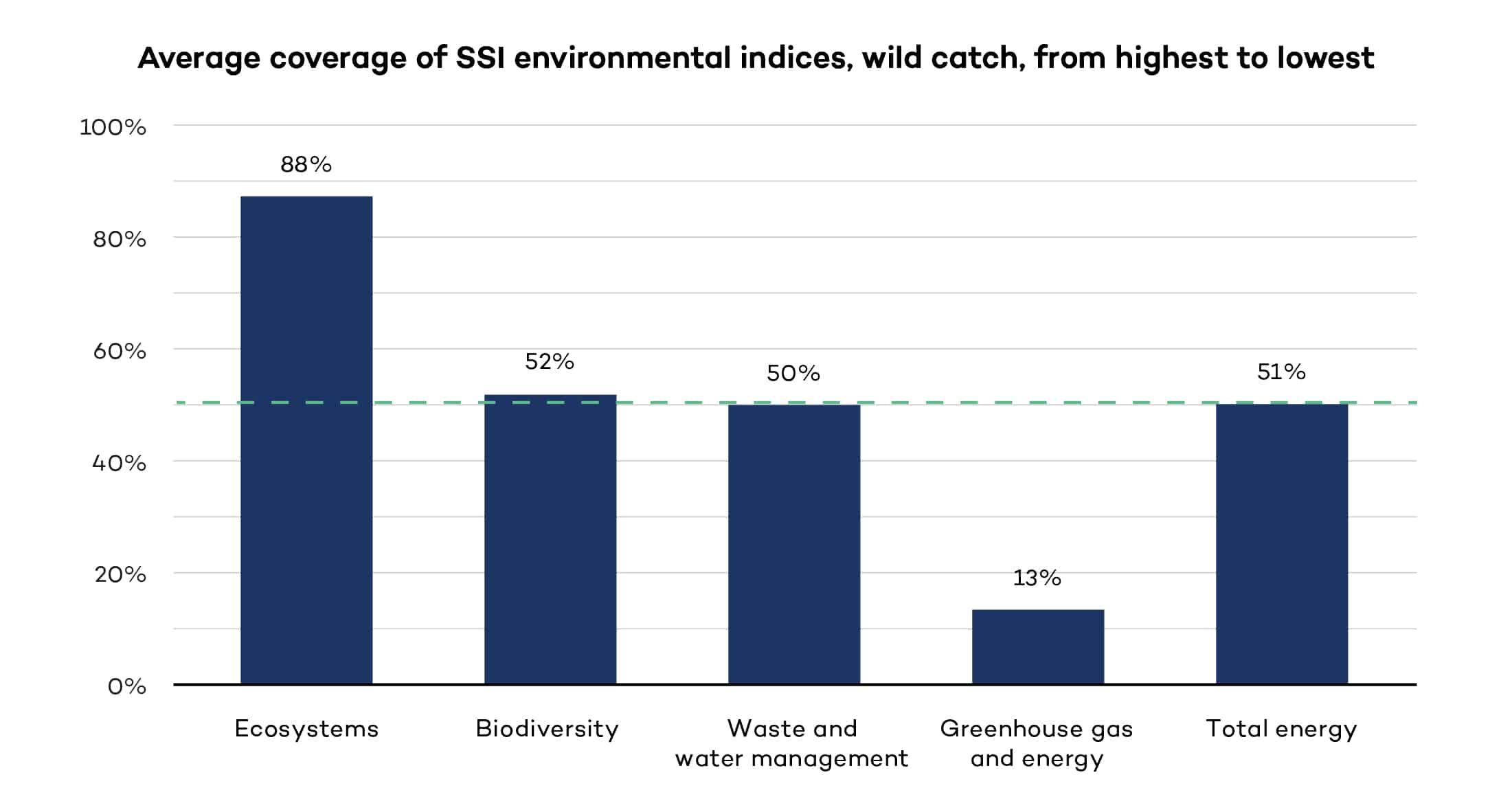)
Protecting wild catch ecosystems
We analyze the environmental sustainability criteria of the 10 voluntary sustainability standards covered in this report to understand how they protect ecosystems, mitigate biodiversity loss, contribute to efficient energy use and limit greenhouse gas emissions in the wild catch sector. This figure presents the key findings in aggregate form.
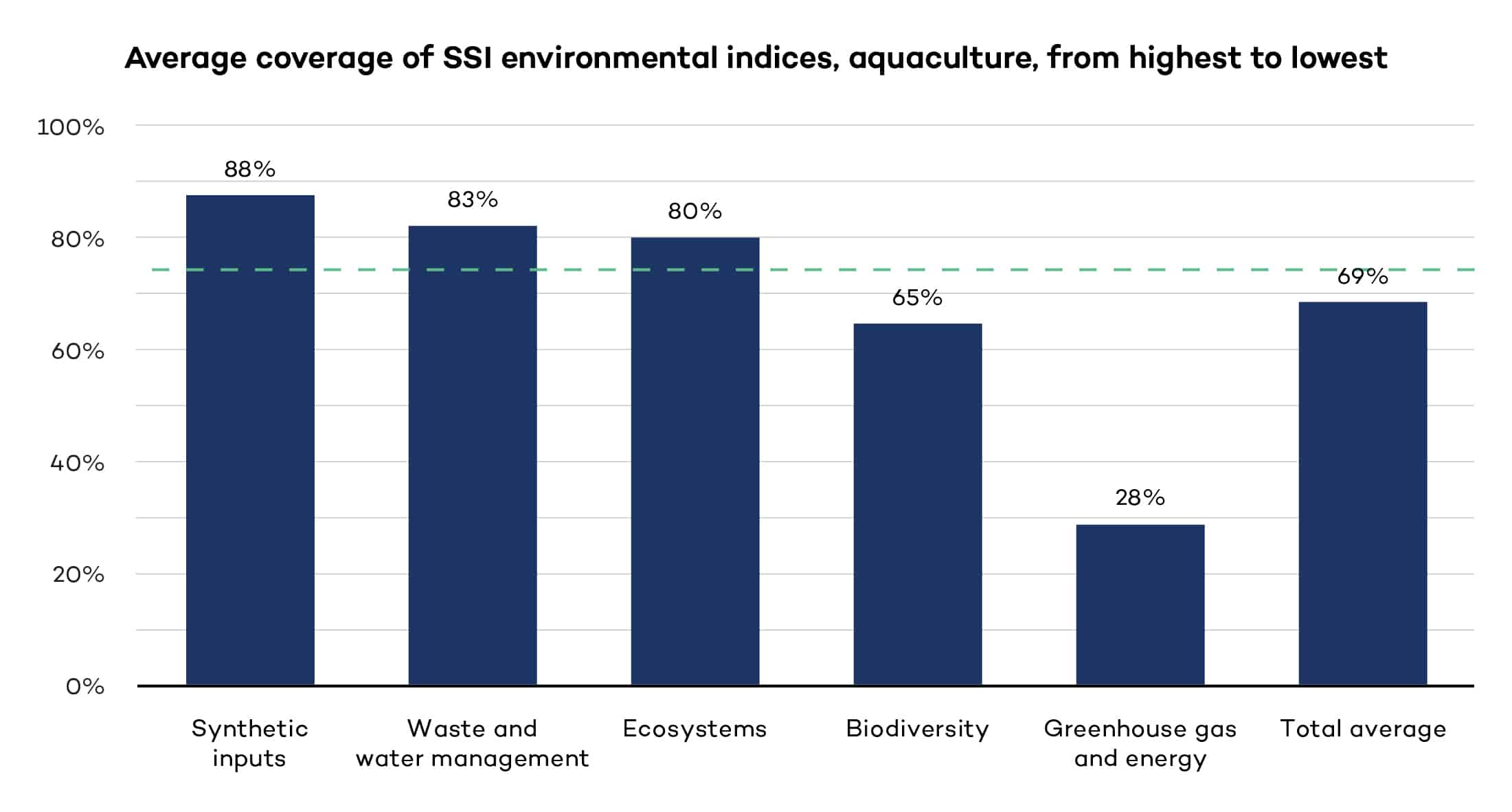)
Protecting aquaculture ecosystems
We examine the environmental sustainability criteria of the 10 voluntary sustainability standards covered in this report to understand how they protect ecosystems, mitigate biodiversity loss, manage genetically modified organisms and waste, and limit greenhouse gas emissions in the aquaculture sector. This figure presents the key findings in aggregate form.
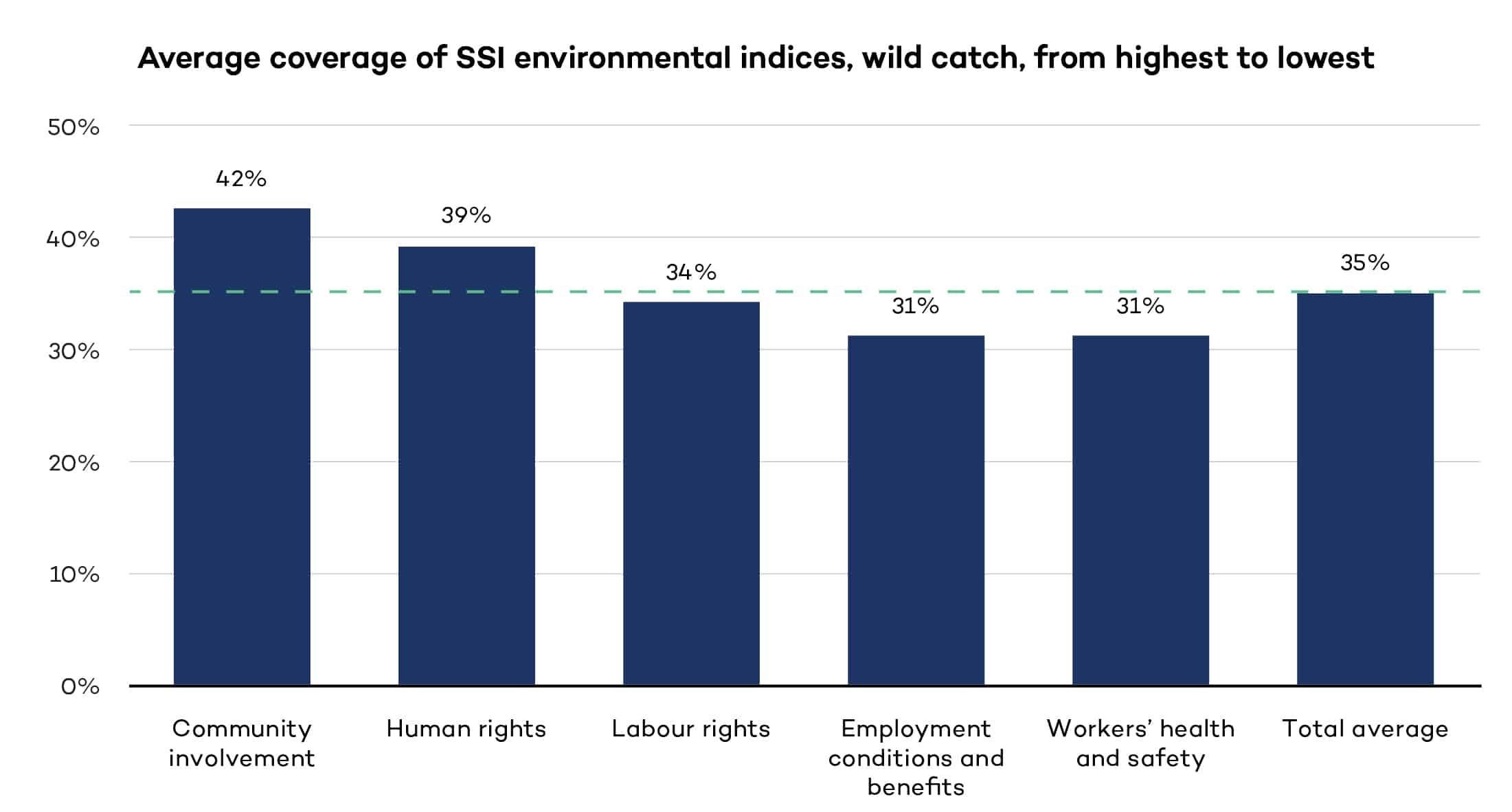)
Fostering socially sustainable practices in wild catch
We assess the social criteria of the 10 voluntary sustainability standards in the wild catch sector to determine their contribution to crucial issues, including labour rights and workers’ health and safety. The findings are presented in aggregate form.
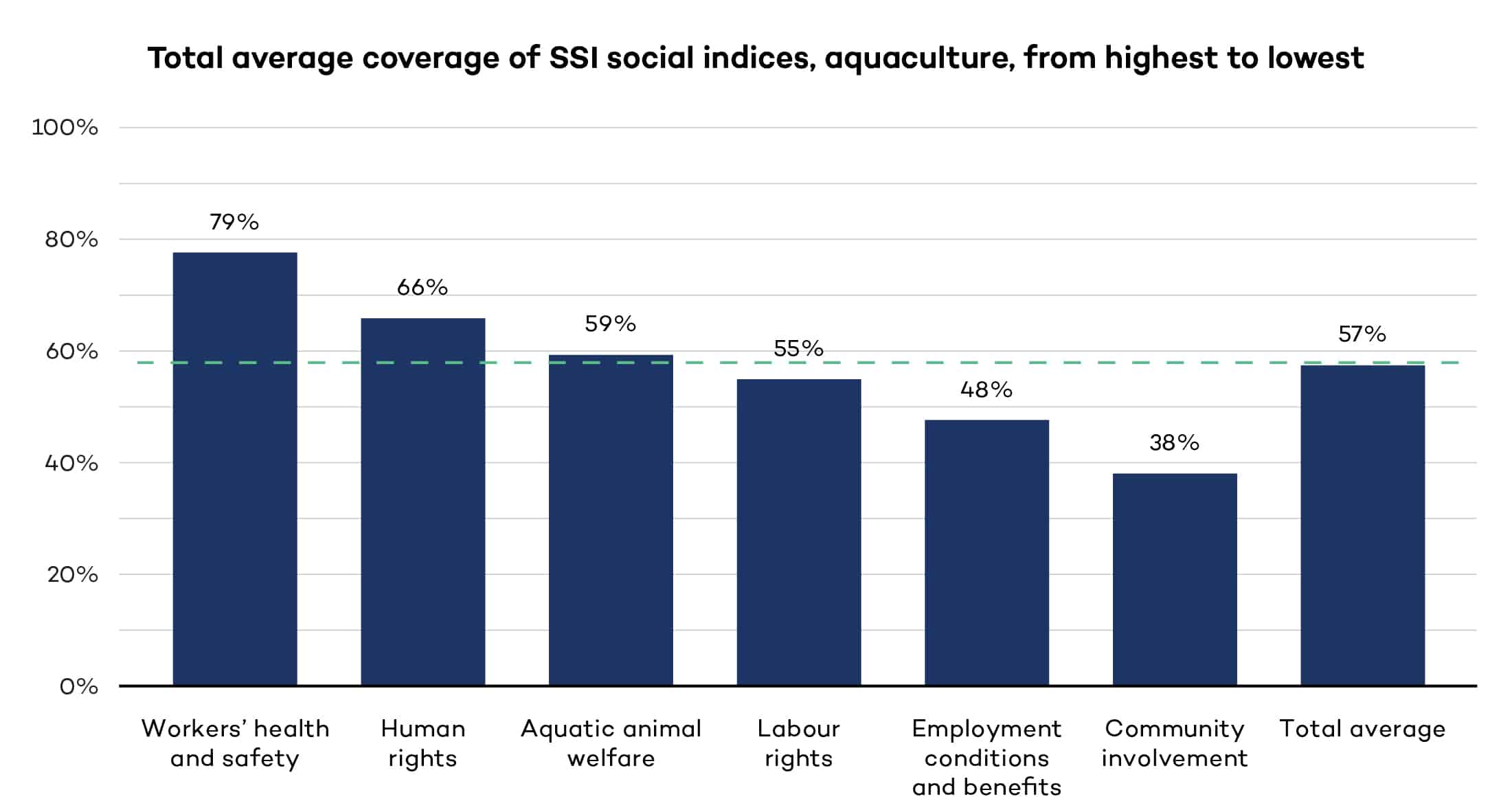)
Fostering socially sustainable practices in aquaculture
From human and labour rights to community involvement, we explore the social criteria of 10 voluntary sustainability standards in the aquaculture sector to determine how they’re contributing to social sustainability. The findings are presented in aggregate form.
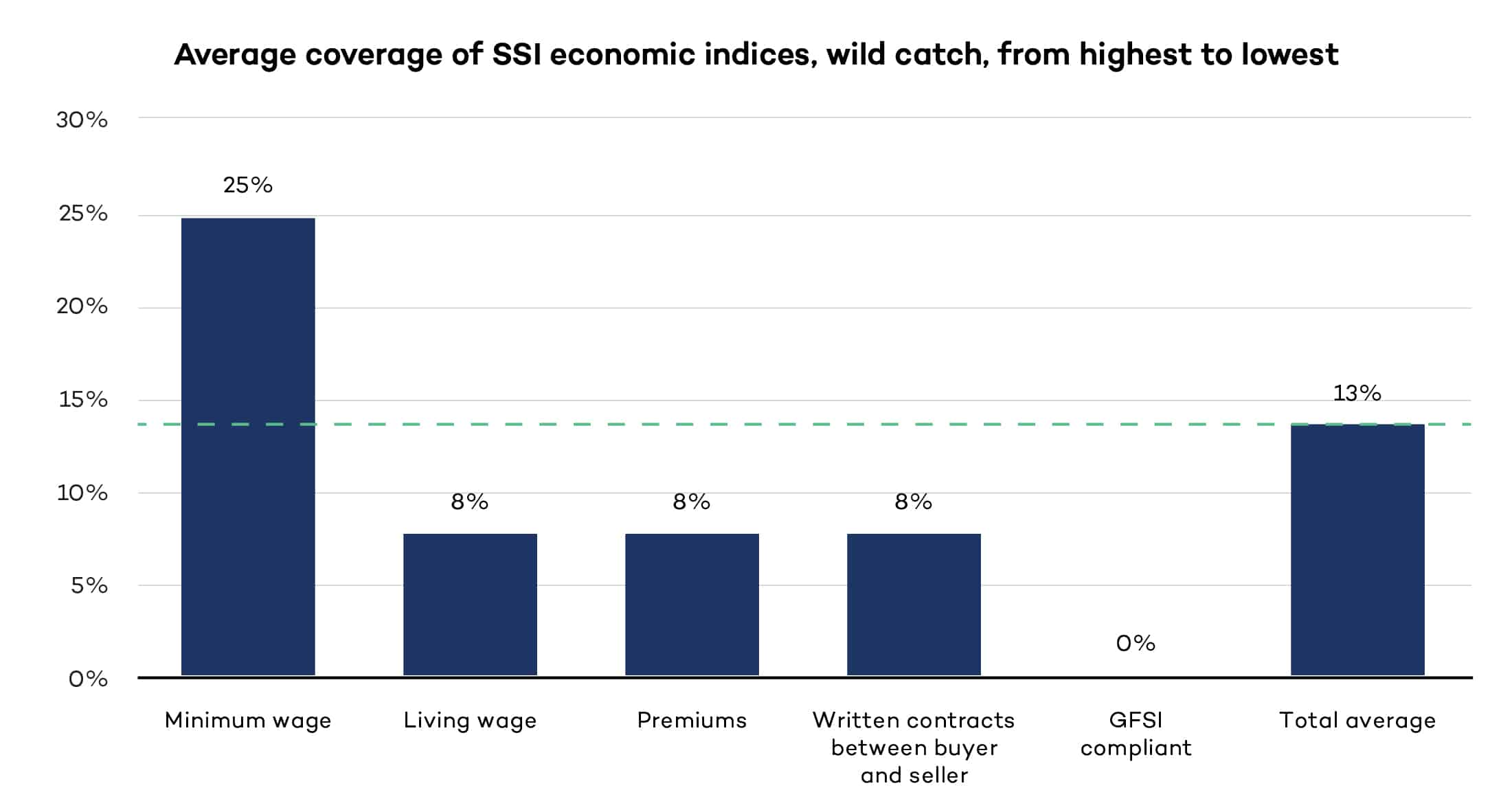)
Contributing to sustainable livelihoods in the wild catch sector
We assess the economic criteria within 10 wild catch standards to determine how they’re contributing to economic sustainability. The findings are presented in aggregate form.
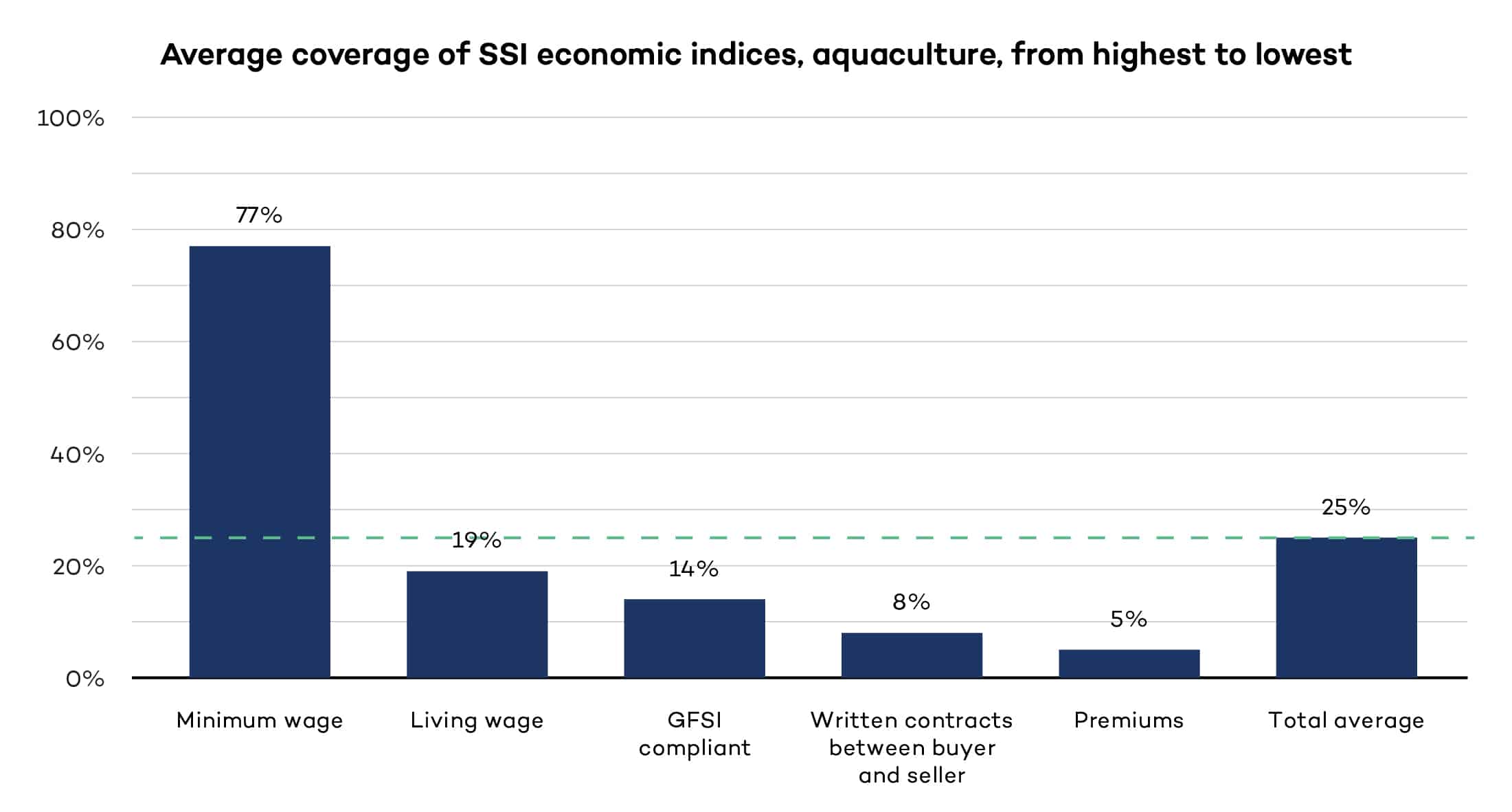)
Contributing to sustainable livelihoods in the aquaculture sector
We examine economic criteria of 10 aquaculture standards to determine their contribution to sustainable development. The findings are presented in aggregate form.

