Standards and Biodiversity
Sustainable agriculture practices must be widely implemented in order to stem an alarming loss of biodiversity and to protect endangered species.
This is according to our SSI Review: Standards and Biodiversity, examining the intersection between voluntary sustainability standards and the conservation of biodiversity.
The study identified several opportunities to leverage the impact of voluntary sustainability standards to prevent and slow biodiversity losses.
There is a clear rationale for policy-makers to support the evolution of voluntary sustainability standards in ways that can help ensure that they play a constructive role in meeting biodiversity targets. Voluntary sustainability standards offer an opportunity to reduce the biodiversity impacts of agriculture while promoting best practices, which can also improve yields and help feed a growing population.
This report was published in 2017 with data inclusive from 2008 to 2014.
USD 52.5 billion
The market value of certified agricultural products was estimated to be USD 52.5 billion in 2015 for eight major commodities, an increased from 2012’s USD 31.6 billion.
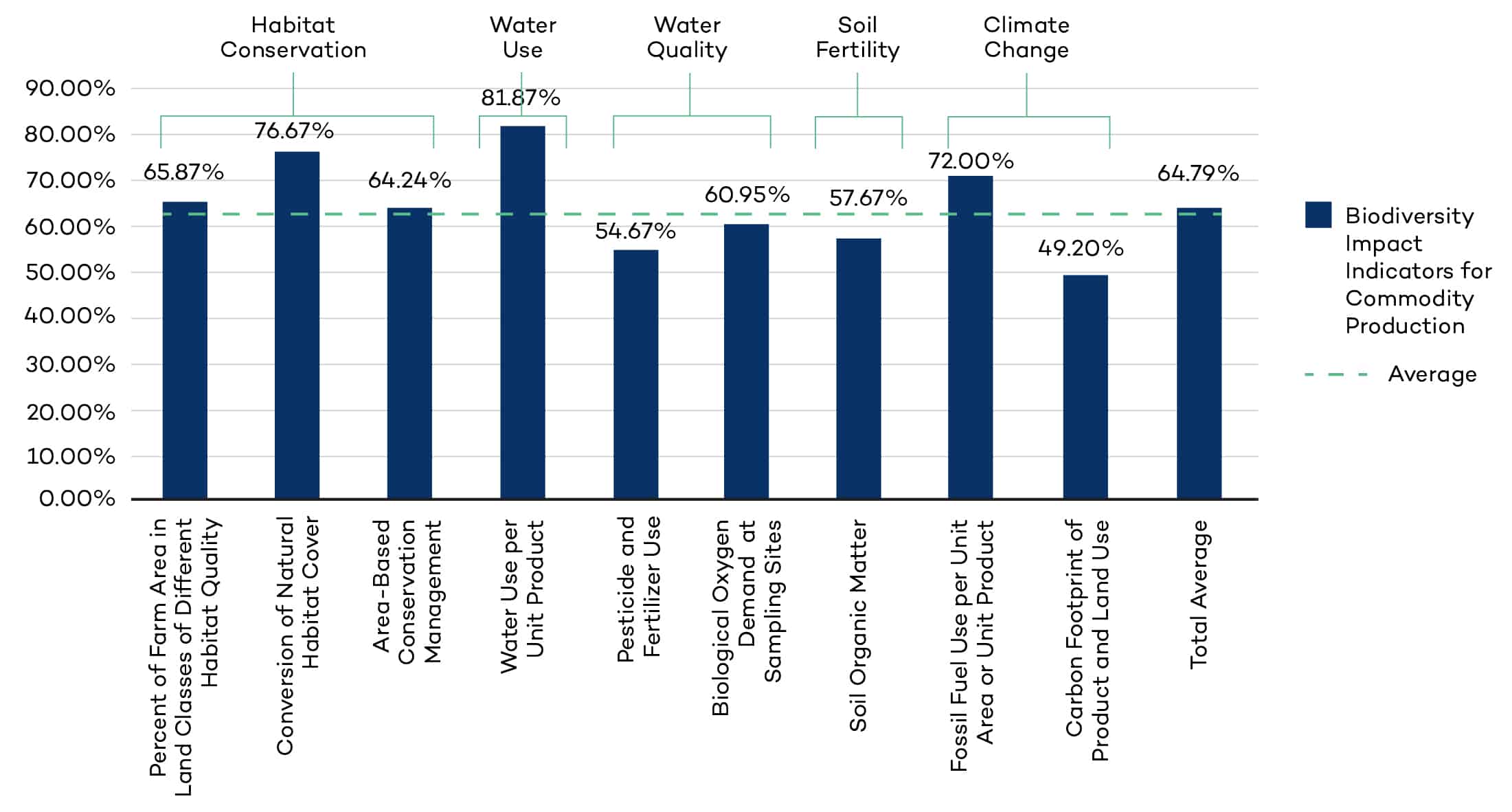)
Biodiversity conservation efforts across the standards
We draw from five major biodiversity-impact related pathways developed by the Conventional on Biological Diversity: habitat conservation, water use, water quality, soil fertility and climate change, to conduct an analysis of voluntary sustainability standards criteria versus the biodiversity impact indicators for commodity production (BIICP) included in these groups to provide a streamlined window for understanding how they contribute to biodiversity protection. This figure presents the key findings in aggregate form.
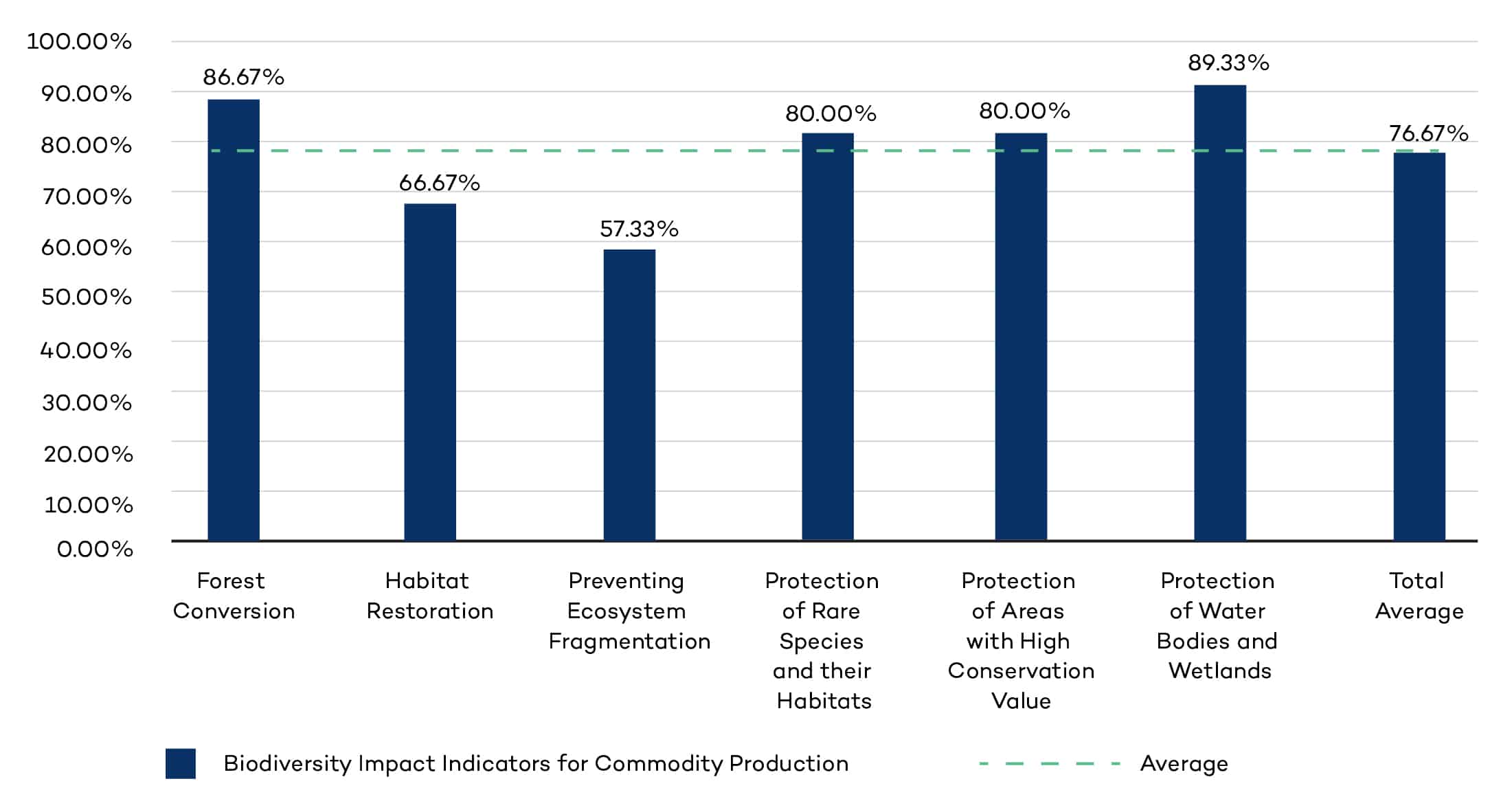)
Protections against the loss of natural habitats
We take a deep dive into the Conversion of Natural Habitat Index to explore how voluntary sustainability standards are contributing to the protection of natural habitats, from habitat restoration to protecting wetlands.
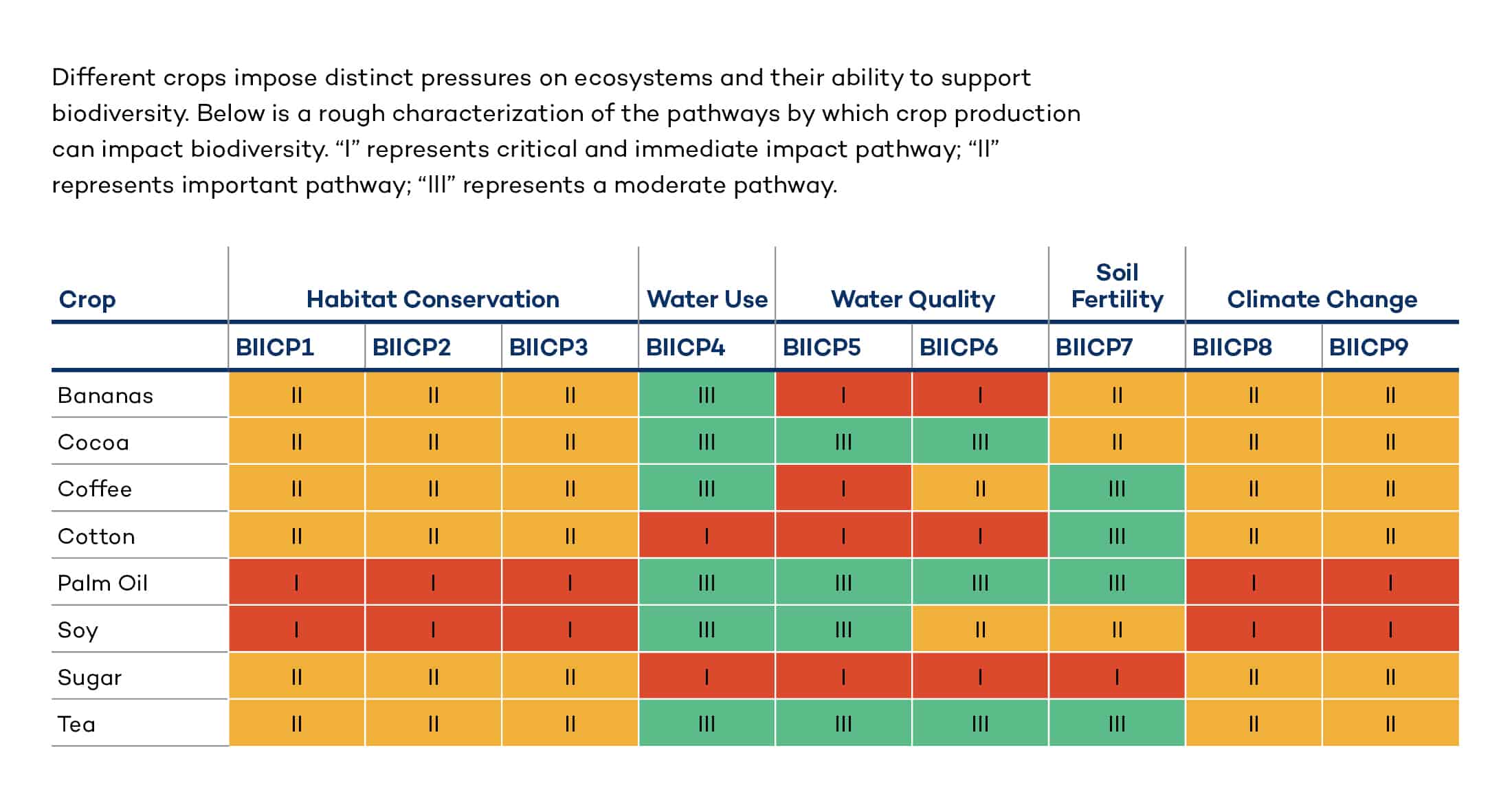)
The varying degrees of different crops impacting ecosystems
We also analyze the impact of certain crops on biodiversity, as different crops impose distinct pressures on ecosystems and differ in their ability to support biodiversity. We’ve provided a rough characterization of the pathways through which crop production can impact biodiversity. “I” represents a critical and immediate impact pathway; “II” represents an important pathway; “III” represents a moderate pathway.

